Why Advanced PFAS Treatment Is Crucial for Eliminating Harmful Chemical Exposure
Why Advanced PFAS Treatment Is Crucial for Eliminating Harmful Chemical Exposure
Blog Article
Advanced Techniques for Reliable PFAS Contamination Removal
The consistent difficulty of PFAS contamination requires the expedition of innovative removal techniques that can properly attend to these damaging substances. Innovative technologies, such as advanced oxidation processes and various adsorption methods, have actually arised as appealing remedies in mitigating PFAS from influenced environments.
Recognizing PFAS Features
Although per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) have actually been widely used in various industrial and consumer items due to their one-of-a-kind homes, their persistence in the atmosphere postures considerable challenges to public health and security. PFAS are a team of artificial chemicals characterized by a carbon-fluorine bond, one of the strongest chemical bonds known, which adds to their exceptional stability and resistance to deterioration. This stability allows PFAS to build up in the environment and living organisms, causing possible damaging health effects.
The hydrophobic and oleophobic nature of PFAS makes them specifically effective in applications such as non-stick coatings, stain-resistant fabrics, and firefighting foams. However, these very same homes contribute to their environmental persistence, as PFAS do not easily break down via all-natural processes. In addition, their extensive use has actually led to common contamination of water resources and dirts, making complex remediation initiatives. Recognizing the chemical residential or commercial properties of PFAS is vital for developing efficient techniques to take care of and reduce their ecological effect. The distinct characteristics of these compounds demand a nuanced strategy to address the challenges positioned by their presence in ecological communities and possible human direct exposure.
Innovative Remediation Technologies
The persistence of PFAS in the environment has spurred the advancement of ingenious remediation innovations focused on effectively removing these pollutants from affected ecological communities. Among the most promising approaches are innovative oxidation processes (AOPs), which make use of effective oxidants to break down PFAS compounds right into less hazardous materials. AOPs can be tailored to target particular PFAS structures, boosting their efficacy.
One more arising innovation is using adsorption media, such as turned on carbon and ion exchange resins, which can selectively record PFAS from polluted water. These materials have shown significant removal efficiencies, although routine substitute and regrowth are necessary to preserve performance.
Membrane layer filtration methods, consisting of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, are also acquiring traction in PFAS removal. These methods can effectively divide PFAS from water, offering a sensible service for treating polluted resources. In addition, thermal treatment methods, such as incineration, can disintegrate PFAS right into non-toxic by-products, though they require cautious monitoring to control emissions.
Collectively, these cutting-edge remediation innovations represent substantial improvements in the recurring fight versus PFAS contamination, supplying various approaches to restore afflicted settings and secure public wellness.

Bioremediation Strategies
Bioremediation methods use an appealing technique to resolving PFAS contamination by taking advantage of the natural capabilities of microbes to degrade these persistent substances (m270 waste management). This approach involves using bacteria, fungis, and other germs that can metabolize or transform PFAS materials right into less dangerous byproducts
Recent improvements in molecular biology and environmental microbiology have actually enhanced our understanding of microbial areas and their potential roles in PFAS degradation. Scientists are actively checking out certain pressures of germs, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus, which have actually shown the capacity to damage down certain PFAS substances.
Sitting bioremediation strategies, where bacteria are stimulated see this here directly in contaminated environments, can be particularly effective. This strategy usually includes the application of nutrients or electron benefactors to advertise microbial growth and task. Furthermore, ex situ techniques, such as bioreactors, permit controlled problems that can enhance destruction rates.
Despite the assurance of bioremediation, difficulties stay, consisting of the intricate nature of PFAS substances and the need for extensive field screening - m270 waste management. Continued study and growth will certainly be essential to fine-tune visite site these strategies and examine their effectiveness in varied ecological contexts
Adsorption and Filtering Approaches
Attending to PFAS contamination usually entails employing adsorption and purification methods, which are created to get rid of these persistent chemicals from water and soil. Amongst the various strategies, activated carbon adsorption is widely utilized because of its high surface and porosity, making it possible for effective trapping of PFAS particles. Granular triggered carbon (GAC) systems are especially preferred for dealing with large volumes of contaminated water, while powdered turned on carbon (POLITICAL ACTION COMMITTEE) can be made use of for smaller-scale applications.
Ion exchange materials also reveal promise in PFAS removal, functioning by trading PFAS ions with less damaging ions in the water. This approach has demonstrated performance in focusing PFAS compounds, promoting their succeeding removal. Furthermore, membrane layer filtering strategies, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, operate by making use of semi-permeable membranes to different PFAS from water, successfully lowering their concentrations.
While these techniques work, they need to be meticulously picked based upon the specific PFAS substances present and the ecological context. Constant advancements in materials scientific research and design are resulting in the growth of unique adsorbents and filtering systems that improve removal effectiveness and lower functional costs, thus improving general remediation efforts.
Regulatory and Plan Considerations
How can reliable regulatory frameworks enhance the management of PFAS contamination? Extensive plans are necessary to guarantee a coordinated more information and robust response to the challenges posed by per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) Laws can develop clear standards for surveillance, reporting, and remediating PFAS-contaminated sites, cultivating liability amongst industries and public entities. (m270 waste management)
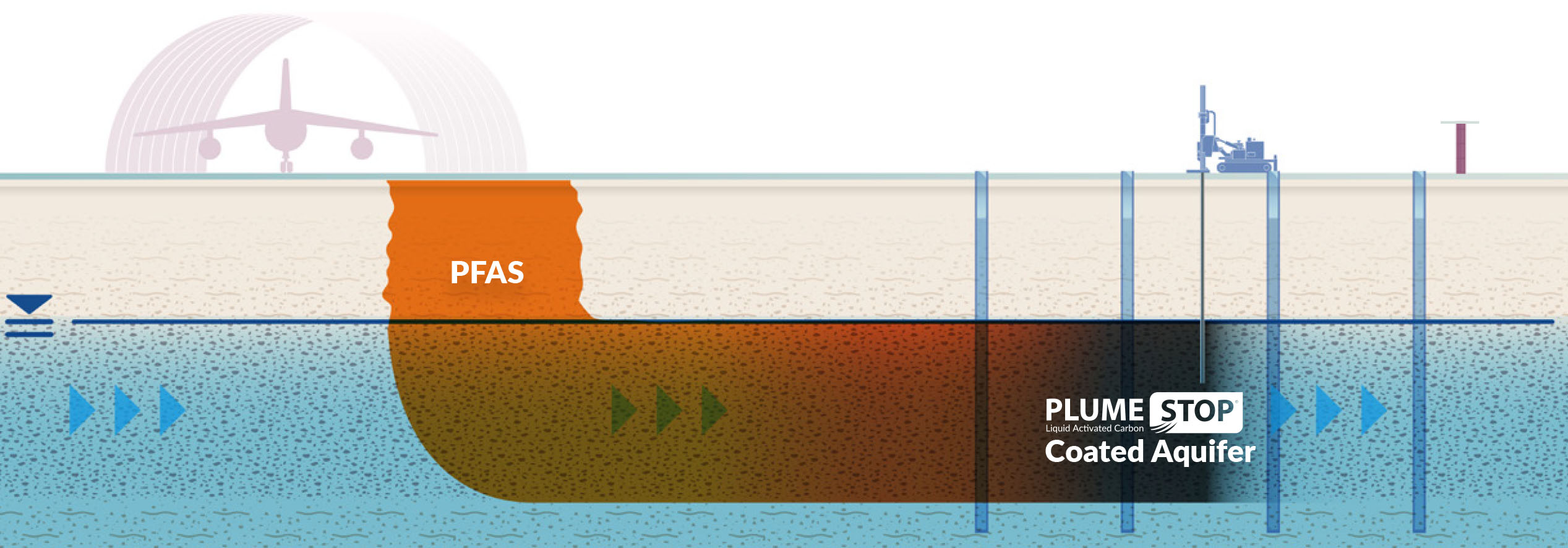
In addition, economic incentives and grants can be incorporated into policies to motivate the adoption of innovative removal innovations. Policymakers ought to likewise focus on research study and development, guaranteeing that arising techniques for PFAS elimination are confirmed and implemented properly.
In addition, public understanding and interaction are important parts of any type of governing technique, empowering communities to support for their health and wellness. Ultimately, a well-structured regulative setting will not only boost the monitoring of PFAS contamination yet additionally promote sustainable techniques that secure future generations.
Conclusion
In summary, the complexity of PFAS contamination requires the fostering of advanced remediation methods. Ingenious innovations such as advanced oxidation procedures, adsorption methods, and membrane filtration have shown substantial efficiency in eliminating these relentless compounds from contaminated water resources. In addition, regulative structures have to evolve to support the execution of these technologies, making sure risk-free and effective monitoring of PFAS toxins. Proceeded study and growth in this field continue to be essential to dealing with the challenges positioned by PFAS contamination.
Report this page